
Boolean offer() – inserts a new element into the queue if it is possible.As interface’s methods they should be represented in all classes that implement Queue. Queue Methods JavaThe Queue declares a number of methods. Queue implements Iterable interface, that allows an object to be the target of the "for-each loop" statement. So it supports all methods of Collection interface such as insertion, deletion and so on. What does it mean? First of all, Java Queue is a part of the Collection Framework and implements Collection interface. According to Oracle documentation, Queue interface has 2 superinterfaces, 4 different interfaces that inherit from the queue, and an extremely impressive list of classes.īlockingDeque, BlockingQueue, Deque, TransferQueueĪbstractQueue, ArrayBlockingQueue, ArrayDeque, ConcurrentLinkedDeque, ConcurrentLinkedQueue, DelayQueue, LinkedBlockingDeque, LinkedBlockingQueue, LinkedList, LinkedTransferQueue, PriorityBlockingQueue, PriorityQueue, SynchronousQueue Queue in JavaQueue in Java is an interface. This is the main principle of classical queue data structure work. So, while working with a queue, new elements are added to the end, and if you want to get an element, it will be taken from the beginning. If the new customer comes, he/she will be the 5th in line to get hamburgers. If you have four people in line in McDonalds or elsewhere, the first to line up will be the first to get the store. The customer that came first, is going to be served first as well. It seems like a queue or a line of customers in real life.

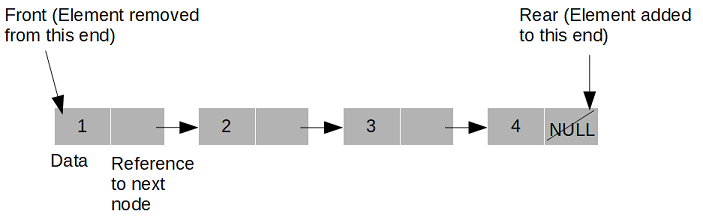
You may imagine Queue data structure very easily. That means you can add an element (or enqueue, put in the queue) only at the end of the structure, and take an element (dequeue or remove from the queue) only from its beginning. Queue data structureA Queue is a linear abstract data structure with the particular order of performing operations - First In First Out (FIFO). After that, we take a closer look at the most important implementations and learn them with examples. Also, what implementations of Queue are in Java language. You’ll find out what Queue data structure is, how it is represented in Java, what methods are the most important for all queues. * LinkedQueue.Here we are going to discuss the Java Queue interface. IsEmpty(): Returns true if queue is empty, false otherwise.
Size(): Return the number of items the queue contains right now. The following methods we plan to implement as part of our linked list implementation of queue in Java. In linked implementation of queue we will keep front and rear pointing at beginning and end of the queue.Ī queue by definition supports two methods, one is enqueue (also called insert) for adding objects to the queue, and second, dequeue (also called delete) for removing an item from the queue. The front pointer points to the end where items are removed from, while the rear points to the end where items are added to the queue. A queue usually has two ends, one for adding items and another for removing them, these ends are pointed by two pointers called front and rear. A queue is a container to which items are added and removed by following first-in-first-out strategy therefore, an item added to the container first will be removed first.

Here, we implement a generic queue in Java using linked list. Linked List Implementation of Queue in Java Iterating through Queue Items - Queue Iterator.Linked List Implementation of Queue in Java.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
